Welcome to Software Development on Codidact!
Will you help us build our independent community of developers helping developers? We're small and trying to grow. We welcome questions about all aspects of software development, from design to code to QA and more. Got questions? Got answers? Got code you'd like someone to review? Please join us.
Post History
It is a common mistake is to mix up the concepts of operator precedence and order of evaluation. Beginner classes and books often address the former in detail, but forget to mention the latter at a...
Answer
#5: Post edited
- It is a common mistake is to mix up the concepts of operator precedence and order of evaluation. Beginner classes and books often address the former in detail, but forget to mention the latter at all.
- _Operator precedence_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _parsed_. It is similar to the use of operators in mathematics and tells us which operand that belongs ("glues") to which operator. In an expression such as `a + b * c`, operator precedence specifies that the expression must be treated as equivalent to `a + (b * c)`.
- _Order of evaluation_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _executed_. That is the order in which the functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` are executed. It is obvious that `b()` and `c()` must be called before `b() * c()` can be calculated, but it is less obvious that all three functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` might be called in advance and that a() might be called first. The order in which they are called/executed is the order of evaluation.
- Each operator in C and C++ specifies such an order of evaluation of its operands (given that it has more than 1 operand). In the general case, the order of evaluation is _unspecified behavior_, a formal term in C and C++ which means that the language standard leaves the order to the compiler. But the compiler need not document it to the programmer and the programmer can't know it and shouldn't rely on it. It can even be different from line to line in the same program.
- The rationale<sup>1)</sup> behind this is to allow compilers to keep their expression parsing algorithm a trade secret, since this affects both program execution speed and time to compile. Internally, compilers go through the expression by building up an expression parser tree, similar to this:
- 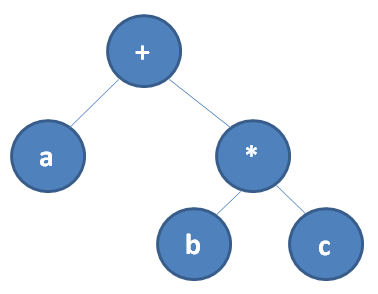
- The operator precedence specify how this expression tree should be built up, but the order of evaluation specifies the order this tree is traversed - could either be left-to-right or right-to-left, and it might even make sense to do it in a different order from case to case basis.
Newer C and C++ standards formally states that (example from C17 6.5/3)- > The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax. Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced.
- This cryptic little text summarizes all of the things above. "The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax." refers to operator precedence, which is very hard to understand from reading the standard syntax alone. That is why programmers often use informal so-called "precedence tables" to easier summarize the precedence rules and operator groups.
- The second sentence "Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced." is what specifies that order of evaluation as unspecified behavior for most operators in the language. "Except as specified later" refers to special case operators that guarantee a certain order of evaluation. Those are for example the operators `&&`, `||`, `?:` and `,`, all which have special left-to-right execution guarantees. C++17 and beyond also have special guarantees for the assignment operators. The majority of operators do not have any such guarantees though.
- What all this means in practice is that we should never write code which relies on a certain order of evaluation.
- Note that order of evaluation also applies to a variable initalizer lists: `int arr[] = {a(), b()};` has no defined order of evaluation. And similarly, function argument evaluation order is also unspecified.
- ---
- <sup>1)</sup> _Rationale for International Standard - Programming Languages - C. Revision 5.10 April-2003_, 3/25:
- > The terms _unspecified behavior_, _undefined behavior_, and _implementation-defined behavior_ are
- used to categorize the result of writing programs whose properties the Standard does not, or cannot, completely describe. The goal of adopting this categorization is to allow a certain
- variety among implementations which permits quality of implementation to be an active force in
- the marketplace as well as to allow certain popular extensions, without removing the cachet of
- conformance to the Standard.
- >
- > _Unspecified behavior_ gives the implementor some latitude in translating programs. This latitude
- does not extend as far as failing to translate the program, however, because all possible behaviors
- are “correct” in the sense that they don’t cause undefined behavior in any implementation.
- It is a common mistake is to mix up the concepts of operator precedence and order of evaluation. Beginner classes and books often address the former in detail, but forget to mention the latter at all.
- _Operator precedence_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _parsed_. It is similar to the use of operators in mathematics and tells us which operand that belongs ("glues") to which operator. In an expression such as `a + b * c`, operator precedence specifies that the expression must be treated as equivalent to `a + (b * c)`.
- _Order of evaluation_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _executed_. That is the order in which the functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` are executed. It is obvious that `b()` and `c()` must be called before `b() * c()` can be calculated, but it is less obvious that all three functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` might be called in advance and that a() might be called first. The order in which they are called/executed is the order of evaluation.
- Each operator in C and C++ specifies such an order of evaluation of its operands (given that it has more than 1 operand). In the general case, the order of evaluation is _unspecified behavior_, a formal term in C and C++ which means that the language standard leaves the order to the compiler. But the compiler need not document it to the programmer and the programmer can't know it and shouldn't rely on it. It can even be different from line to line in the same program.
- The rationale<sup>1)</sup> behind this is to allow compilers to keep their expression parsing algorithm a trade secret, since this affects both program execution speed and time to compile. Internally, compilers go through the expression by building up an expression parser tree, similar to this:
- 
- The operator precedence specify how this expression tree should be built up, but the order of evaluation specifies the order this tree is traversed - could either be left-to-right or right-to-left, and it might even make sense to do it in a different order from case to case basis.
- Newer C and C++ standards formally state that (example from C17 6.5/3)
- > The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax. Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced.
- This cryptic little text summarizes all of the things above. "The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax." refers to operator precedence, which is very hard to understand from reading the standard syntax alone. That is why programmers often use informal so-called "precedence tables" to easier summarize the precedence rules and operator groups.
- The second sentence "Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced." is what specifies that order of evaluation as unspecified behavior for most operators in the language. "Except as specified later" refers to special case operators that guarantee a certain order of evaluation. Those are for example the operators `&&`, `||`, `?:` and `,`, all which have special left-to-right execution guarantees. C++17 and beyond also have special guarantees for the assignment operators. The majority of operators do not have any such guarantees though.
- What all this means in practice is that we should never write code which relies on a certain order of evaluation.
- Note that order of evaluation also applies to a variable initalizer lists: `int arr[] = {a(), b()};` has no defined order of evaluation. And similarly, function argument evaluation order is also unspecified.
- ---
- <sup>1)</sup> _Rationale for International Standard - Programming Languages - C. Revision 5.10 April-2003_, 3/25:
- > The terms _unspecified behavior_, _undefined behavior_, and _implementation-defined behavior_ are
- used to categorize the result of writing programs whose properties the Standard does not, or cannot, completely describe. The goal of adopting this categorization is to allow a certain
- variety among implementations which permits quality of implementation to be an active force in
- the marketplace as well as to allow certain popular extensions, without removing the cachet of
- conformance to the Standard.
- >
- > _Unspecified behavior_ gives the implementor some latitude in translating programs. This latitude
- does not extend as far as failing to translate the program, however, because all possible behaviors
- are “correct” in the sense that they don’t cause undefined behavior in any implementation.
#4: Post edited
- It is a common mistake is to mix up the concepts of operator precedence and order of evaluation. Beginner classes and books often address the former in detail, but forget to mention the latter at all.
- _Operator precedence_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _parsed_. It is similar to the use of operators in mathematics and tells us which operand that belongs ("glues") to which operator. In an expression such as `a + b * c`, operator precedence specifies that the expression must be treated as equivalent to `a + (b * c)`.
- _Order of evaluation_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _executed_. That is the order in which the functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` are executed. It is obvious that `b()` and `c()` must be called before `b() * c()` can be calculated, but it is less obvious that all three functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` might be called in advance and that a() might be called first. The order in which they are called/executed is the order of evaluation.
- Each operator in C and C++ specifies such an order of evaluation of its operands (given that it has more than 1 operand). In the general case, the order of evaluation is _unspecified behavior_, a formal term in C and C++ which means that the language standard leaves the order to the compiler. But the compiler need not document it to the programmer and the programmer can't know it and shouldn't rely on it. It can even be different from line to line in the same program.
- The rationale<sup>1)</sup> behind this is to allow compilers to keep their expression parsing algorithm a trade secret, since this affects both program execution speed and time to compile. Internally, compilers go through the expression by building up an expression parser tree, similar to this:
- 
- The operator precedence specify how this expression tree should be built up, but the order of evaluation specifies the order this tree is traversed - could either be left-to-right or right-to-left, and it might even make sense to do it in a different order from case to case basis.
- Newer C and C++ standards formally states that (example from C17 6.5/3)
- > The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax. Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced.
- This cryptic little text summarizes all of the things above. "The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax." refers to operator precedence, which is very hard to understand from reading the standard syntax alone. That is why programmers often use informal so-called "precedence tables" to easier summarize the precedence rules and operator groups.
- The second sentence "Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced." is what specifies that order of evaluation as unspecified behavior for most operators in the language. "Except as specified later" refers to special case operators that guarantee a certain order of evaluation. Those are for example the operators `&&`, `||`, `?:` and `,`, all which have special left-to-right execution guarantees. C++17 and beyond also have special guarantees for the assignment operators. The majority of operators do not have any such guarantees though.
- What all this means in practice is that we should never write code which relies on a certain order of evaluation.
- Note that order of evaluation also applies to a variable initalizer lists: `int arr[] = {a(), b()};` has no defined order of evaluation. And similarly, function argument evaluation order is also unspecified.
- ---
- <sup>1)</sup> _Rationale for International Standard - Programming Languages - C. Revision 5.10 April-2003_, 3/25:
- > The terms _unspecified behavior_, _undefined behavior_, and _implementation-defined behavior_ are
- used to categorize the result of writing programs whose properties the Standard does not, or cannot, completely describe. The goal of adopting this categorization is to allow a certain
- variety among implementations which permits quality of implementation to be an active force in
- the marketplace as well as to allow certain popular extensions, without removing the cachet of
conformance to the Standard.
- It is a common mistake is to mix up the concepts of operator precedence and order of evaluation. Beginner classes and books often address the former in detail, but forget to mention the latter at all.
- _Operator precedence_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _parsed_. It is similar to the use of operators in mathematics and tells us which operand that belongs ("glues") to which operator. In an expression such as `a + b * c`, operator precedence specifies that the expression must be treated as equivalent to `a + (b * c)`.
- _Order of evaluation_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _executed_. That is the order in which the functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` are executed. It is obvious that `b()` and `c()` must be called before `b() * c()` can be calculated, but it is less obvious that all three functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` might be called in advance and that a() might be called first. The order in which they are called/executed is the order of evaluation.
- Each operator in C and C++ specifies such an order of evaluation of its operands (given that it has more than 1 operand). In the general case, the order of evaluation is _unspecified behavior_, a formal term in C and C++ which means that the language standard leaves the order to the compiler. But the compiler need not document it to the programmer and the programmer can't know it and shouldn't rely on it. It can even be different from line to line in the same program.
- The rationale<sup>1)</sup> behind this is to allow compilers to keep their expression parsing algorithm a trade secret, since this affects both program execution speed and time to compile. Internally, compilers go through the expression by building up an expression parser tree, similar to this:
- 
- The operator precedence specify how this expression tree should be built up, but the order of evaluation specifies the order this tree is traversed - could either be left-to-right or right-to-left, and it might even make sense to do it in a different order from case to case basis.
- Newer C and C++ standards formally states that (example from C17 6.5/3)
- > The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax. Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced.
- This cryptic little text summarizes all of the things above. "The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax." refers to operator precedence, which is very hard to understand from reading the standard syntax alone. That is why programmers often use informal so-called "precedence tables" to easier summarize the precedence rules and operator groups.
- The second sentence "Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced." is what specifies that order of evaluation as unspecified behavior for most operators in the language. "Except as specified later" refers to special case operators that guarantee a certain order of evaluation. Those are for example the operators `&&`, `||`, `?:` and `,`, all which have special left-to-right execution guarantees. C++17 and beyond also have special guarantees for the assignment operators. The majority of operators do not have any such guarantees though.
- What all this means in practice is that we should never write code which relies on a certain order of evaluation.
- Note that order of evaluation also applies to a variable initalizer lists: `int arr[] = {a(), b()};` has no defined order of evaluation. And similarly, function argument evaluation order is also unspecified.
- ---
- <sup>1)</sup> _Rationale for International Standard - Programming Languages - C. Revision 5.10 April-2003_, 3/25:
- > The terms _unspecified behavior_, _undefined behavior_, and _implementation-defined behavior_ are
- used to categorize the result of writing programs whose properties the Standard does not, or cannot, completely describe. The goal of adopting this categorization is to allow a certain
- variety among implementations which permits quality of implementation to be an active force in
- the marketplace as well as to allow certain popular extensions, without removing the cachet of
- conformance to the Standard.
- >
- > _Unspecified behavior_ gives the implementor some latitude in translating programs. This latitude
- does not extend as far as failing to translate the program, however, because all possible behaviors
- are “correct” in the sense that they don’t cause undefined behavior in any implementation.
#3: Post edited
- It is a common mistake is to mix up the concepts of operator precedence and order of evaluation. Beginner classes and books often address the former in detail, but forget to mention the latter at all.
- _Operator precedence_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _parsed_. It is similar to the use of operators in mathematics and tells us which operand that belongs ("glues") to which operator. In an expression such as `a + b * c`, operator precedence specifies that the expression must be treated as equivalent to `a + (b * c)`.
- _Order of evaluation_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _executed_. That is the order in which the functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` are executed. It is obvious that `b()` and `c()` must be called before `b() * c()` can be calculated, but it is less obvious that all three functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` might be called in advance and that a() might be called first. The order in which they are called/executed is the order of evaluation.
- Each operator in C and C++ specifies such an order of evaluation of its operands (given that it has more than 1 operand). In the general case, the order of evaluation is _unspecified behavior_, a formal term in C and C++ which means that the language standard leaves the order to the compiler. But the compiler need not document it to the programmer and the programmer can't know it and shouldn't rely on it. It can even be different from line to line in the same program.
The rationale behind this is to allow compilers to keep their expression parsing algorithm a trade secret, since this affects both program execution speed and time to compile. Internally, compilers go through the expression by building up an expression parser tree, similar to this:- 
- The operator precedence specify how this expression tree should be built up, but the order of evaluation specifies the order this tree is traversed - could either be left-to-right or right-to-left, and it might even make sense to do it in a different order from case to case basis.
- Newer C and C++ standards formally states that (example from C17 6.5/3)
- > The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax. Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced.
- This cryptic little text summarizes all of the things above. "The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax." refers to operator precedence, which is very hard to understand from reading the standard syntax alone. That is why programmers often use informal so-called "precedence tables" to easier summarize the precedence rules and operator groups.
- The second sentence "Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced." is what specifies that order of evaluation as unspecified behavior for most operators in the language. "Except as specified later" refers to special case operators that guarantee a certain order of evaluation. Those are for example the operators `&&`, `||`, `?:` and `,`, all which have special left-to-right execution guarantees. C++17 and beyond also have special guarantees for the assignment operators. The majority of operators do not have any such guarantees though.
- What all this means in practice is that we should never write code which relies on a certain order of evaluation.
Note that order of evaluation also applies to a variable initalizer lists: `int arr[] = {a(), b()};` has no defined order of evaluation. And similarly, function argument evaluation order is also unspecified.
- It is a common mistake is to mix up the concepts of operator precedence and order of evaluation. Beginner classes and books often address the former in detail, but forget to mention the latter at all.
- _Operator precedence_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _parsed_. It is similar to the use of operators in mathematics and tells us which operand that belongs ("glues") to which operator. In an expression such as `a + b * c`, operator precedence specifies that the expression must be treated as equivalent to `a + (b * c)`.
- _Order of evaluation_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _executed_. That is the order in which the functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` are executed. It is obvious that `b()` and `c()` must be called before `b() * c()` can be calculated, but it is less obvious that all three functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` might be called in advance and that a() might be called first. The order in which they are called/executed is the order of evaluation.
- Each operator in C and C++ specifies such an order of evaluation of its operands (given that it has more than 1 operand). In the general case, the order of evaluation is _unspecified behavior_, a formal term in C and C++ which means that the language standard leaves the order to the compiler. But the compiler need not document it to the programmer and the programmer can't know it and shouldn't rely on it. It can even be different from line to line in the same program.
- The rationale<sup>1)</sup> behind this is to allow compilers to keep their expression parsing algorithm a trade secret, since this affects both program execution speed and time to compile. Internally, compilers go through the expression by building up an expression parser tree, similar to this:
- 
- The operator precedence specify how this expression tree should be built up, but the order of evaluation specifies the order this tree is traversed - could either be left-to-right or right-to-left, and it might even make sense to do it in a different order from case to case basis.
- Newer C and C++ standards formally states that (example from C17 6.5/3)
- > The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax. Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced.
- This cryptic little text summarizes all of the things above. "The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax." refers to operator precedence, which is very hard to understand from reading the standard syntax alone. That is why programmers often use informal so-called "precedence tables" to easier summarize the precedence rules and operator groups.
- The second sentence "Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced." is what specifies that order of evaluation as unspecified behavior for most operators in the language. "Except as specified later" refers to special case operators that guarantee a certain order of evaluation. Those are for example the operators `&&`, `||`, `?:` and `,`, all which have special left-to-right execution guarantees. C++17 and beyond also have special guarantees for the assignment operators. The majority of operators do not have any such guarantees though.
- What all this means in practice is that we should never write code which relies on a certain order of evaluation.
- Note that order of evaluation also applies to a variable initalizer lists: `int arr[] = {a(), b()};` has no defined order of evaluation. And similarly, function argument evaluation order is also unspecified.
- ---
- <sup>1)</sup> _Rationale for International Standard - Programming Languages - C. Revision 5.10 April-2003_, 3/25:
- > The terms _unspecified behavior_, _undefined behavior_, and _implementation-defined behavior_ are
- used to categorize the result of writing programs whose properties the Standard does not, or cannot, completely describe. The goal of adopting this categorization is to allow a certain
- variety among implementations which permits quality of implementation to be an active force in
- the marketplace as well as to allow certain popular extensions, without removing the cachet of
- conformance to the Standard.
#2: Post edited
- It is a common mistake is to mix up the concepts of operator precedence and order of evaluation. Beginner classes and books often address the former in detail, but forget to mention the latter at all.
- _Operator precedence_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _parsed_. It is similar to the use of operators in mathematics and tells us which operand that belongs ("glues") to which operator. In an expression such as `a + b * c`, operator precedence specifies that the expression must be treated as equivalent to `a + (b * c)`.
- _Order of evaluation_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _executed_. That is the order in which the functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` are executed. It is obvious that `b()` and `c()` must be called before `b() * c()` can be calculated, but it is less obvious that all three functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` might be called in advance and that a() might be called first. The order in which they are called/executed is the order of evaluation.
- Each operator in C and C++ specifies such an order of evaluation of its operands (given that it has more than 1 operand). In the general case, the order of evaluation is _unspecified behavior_, a formal term in C and C++ which means that the language standard leaves the order to the compiler. But the compiler need not document it to the programmer and the programmer can't know it and shouldn't rely on it. It can even be different from line to line in the same program.
- The rationale behind this is to allow compilers to keep their expression parsing algorithm a trade secret, since this affects both program execution speed and time to compile. Internally, compilers go through the expression by building up an expression parser tree, similar to this:
+a *b c- The operator precedence specify how this expression tree should be built up, but the order of evaluation specifies the order this tree is traversed - could either be left-to-right or right-to-left, and it might even make sense to do it in a different order from case to case basis.
- Newer C and C++ standards formally states that (example from C17 6.5/3)
- > The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax. Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced.
- This cryptic little text summarizes all of the things above. "The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax." refers to operator precedence, which is very hard to understand from reading the standard syntax alone. That is why programmers often use informal so-called "precedence tables" to easier summarize the precedence rules and operator groups.
- The second sentence "Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced." is what specifies that order of evaluation as unspecified behavior for most operators in the language. "Except as specified later" refers to special case operators that guarantee a certain order of evaluation. Those are for example the operators `&&`, `||`, `?:` and `,`, all which have special left-to-right execution guarantees. C++17 and beyond also have special guarantees for the assignment operators. The majority of operators do not have any such guarantees though.
- What all this means in practice is that we should never write code which relies on a certain order of evaluation.
- Note that order of evaluation also applies to a variable initalizer lists: `int arr[] = {a(), b()};` has no defined order of evaluation. And similarly, function argument evaluation order is also unspecified.
- It is a common mistake is to mix up the concepts of operator precedence and order of evaluation. Beginner classes and books often address the former in detail, but forget to mention the latter at all.
- _Operator precedence_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _parsed_. It is similar to the use of operators in mathematics and tells us which operand that belongs ("glues") to which operator. In an expression such as `a + b * c`, operator precedence specifies that the expression must be treated as equivalent to `a + (b * c)`.
- _Order of evaluation_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _executed_. That is the order in which the functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` are executed. It is obvious that `b()` and `c()` must be called before `b() * c()` can be calculated, but it is less obvious that all three functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` might be called in advance and that a() might be called first. The order in which they are called/executed is the order of evaluation.
- Each operator in C and C++ specifies such an order of evaluation of its operands (given that it has more than 1 operand). In the general case, the order of evaluation is _unspecified behavior_, a formal term in C and C++ which means that the language standard leaves the order to the compiler. But the compiler need not document it to the programmer and the programmer can't know it and shouldn't rely on it. It can even be different from line to line in the same program.
- The rationale behind this is to allow compilers to keep their expression parsing algorithm a trade secret, since this affects both program execution speed and time to compile. Internally, compilers go through the expression by building up an expression parser tree, similar to this:
- 
- The operator precedence specify how this expression tree should be built up, but the order of evaluation specifies the order this tree is traversed - could either be left-to-right or right-to-left, and it might even make sense to do it in a different order from case to case basis.
- Newer C and C++ standards formally states that (example from C17 6.5/3)
- > The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax. Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced.
- This cryptic little text summarizes all of the things above. "The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax." refers to operator precedence, which is very hard to understand from reading the standard syntax alone. That is why programmers often use informal so-called "precedence tables" to easier summarize the precedence rules and operator groups.
- The second sentence "Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced." is what specifies that order of evaluation as unspecified behavior for most operators in the language. "Except as specified later" refers to special case operators that guarantee a certain order of evaluation. Those are for example the operators `&&`, `||`, `?:` and `,`, all which have special left-to-right execution guarantees. C++17 and beyond also have special guarantees for the assignment operators. The majority of operators do not have any such guarantees though.
- What all this means in practice is that we should never write code which relies on a certain order of evaluation.
- Note that order of evaluation also applies to a variable initalizer lists: `int arr[] = {a(), b()};` has no defined order of evaluation. And similarly, function argument evaluation order is also unspecified.
#1: Initial revision
It is a common mistake is to mix up the concepts of operator precedence and order of evaluation. Beginner classes and books often address the former in detail, but forget to mention the latter at all.
_Operator precedence_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _parsed_. It is similar to the use of operators in mathematics and tells us which operand that belongs ("glues") to which operator. In an expression such as `a + b * c`, operator precedence specifies that the expression must be treated as equivalent to `a + (b * c)`.
_Order of evaluation_ specifies the order in which an expression should be _executed_. That is the order in which the functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` are executed. It is obvious that `b()` and `c()` must be called before `b() * c()` can be calculated, but it is less obvious that all three functions `a()`, `b()` and `c()` might be called in advance and that a() might be called first. The order in which they are called/executed is the order of evaluation.
Each operator in C and C++ specifies such an order of evaluation of its operands (given that it has more than 1 operand). In the general case, the order of evaluation is _unspecified behavior_, a formal term in C and C++ which means that the language standard leaves the order to the compiler. But the compiler need not document it to the programmer and the programmer can't know it and shouldn't rely on it. It can even be different from line to line in the same program.
The rationale behind this is to allow compilers to keep their expression parsing algorithm a trade secret, since this affects both program execution speed and time to compile. Internally, compilers go through the expression by building up an expression parser tree, similar to this:
+
a *
b c
The operator precedence specify how this expression tree should be built up, but the order of evaluation specifies the order this tree is traversed - could either be left-to-right or right-to-left, and it might even make sense to do it in a different order from case to case basis.
Newer C and C++ standards formally states that (example from C17 6.5/3)
> The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax. Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced.
This cryptic little text summarizes all of the things above. "The grouping of operators and operands is indicated by the syntax." refers to operator precedence, which is very hard to understand from reading the standard syntax alone. That is why programmers often use informal so-called "precedence tables" to easier summarize the precedence rules and operator groups.
The second sentence "Except as specified later, side effects and value computations of subexpressions are unsequenced." is what specifies that order of evaluation as unspecified behavior for most operators in the language. "Except as specified later" refers to special case operators that guarantee a certain order of evaluation. Those are for example the operators `&&`, `||`, `?:` and `,`, all which have special left-to-right execution guarantees. C++17 and beyond also have special guarantees for the assignment operators. The majority of operators do not have any such guarantees though.
What all this means in practice is that we should never write code which relies on a certain order of evaluation.
Note that order of evaluation also applies to a variable initalizer lists: `int arr[] = {a(), b()};` has no defined order of evaluation. And similarly, function argument evaluation order is also unspecified.


















